Archives
- 2026-01
- 2025-12
- 2025-11
- 2025-10
- 2025-09
- 2025-04
- 2025-03
- 2025-02
- 2025-01
- 2024-12
- 2024-11
- 2024-10
- 2024-09
- 2024-08
- 2024-07
- 2024-06
- 2024-05
- 2024-04
- 2024-03
- 2024-02
- 2024-01
- 2023-12
- 2023-11
- 2023-10
- 2023-09
- 2023-08
- 2023-06
- 2023-05
- 2023-04
- 2023-03
- 2023-02
- 2023-01
- 2022-12
- 2022-11
- 2022-10
- 2022-09
- 2022-08
- 2022-07
- 2022-06
- 2022-05
- 2022-04
- 2022-03
- 2022-02
- 2022-01
- 2021-12
- 2021-11
- 2021-10
- 2021-09
- 2021-08
- 2021-07
- 2021-06
- 2021-05
- 2021-04
- 2021-03
- 2021-02
- 2021-01
- 2020-12
- 2020-11
- 2020-10
- 2020-09
- 2020-08
- 2020-07
- 2020-06
- 2020-05
- 2020-04
- 2020-03
- 2020-02
- 2020-01
- 2019-12
- 2019-11
- 2019-10
- 2019-09
- 2019-08
- 2019-07
- 2018-07
-
br Other pathways involved in the preventive and
2021-06-22
Other pathways involved in the preventive and therapeutic potential of flavonoids in neurodegenerative diseases Rather than the induction of MAPK/ERK pathway, flavonoids actively modulate other critical intracellular neuronal survival and death protein kinases pathways, more importantly PI3K/Akt,
-
br Conclusion br Acknowledgments This work was supported by
2021-06-22
Conclusion Acknowledgments This work was supported by Progetto PON - “Ricerca e Competitività 2007–2013” - PON01_01802: “Sviluppo di molecole capaci di modulare vie metaboliche intracellulari redox-sensibili per la prevenzione e la cura di patologie infettive, tumorali, neurodegenerative e lor
-
EP receptors belong to the family of G
2021-06-22
EP1–4 receptors belong to the family of G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). Trafficking events such as externalization, internalization, recycling and degradation dynamically regulate GPCR cell surface density. A fast-rate of internalization and degradation reduces GPCR surface density to desensitize
-
The following are the supplementary data related to this art
2021-06-22
The following are the supplementary data related to this article. Acknowledgments Introduction Cyclooxygenases metabolize arachidonic Spautin-1 to five primary prostanoids, PGE2, PGF2, PGI2, TXA2 (TX), and PGD2. These lipid mediators interact with specific members of a family of distinct G-p
-
In conclusion we demonstrate that infection of salmon
2021-06-21
In conclusion we demonstrate that infection of salmon cells with ISAV induce the main branches of the cellular UPR machinery, but also one of its main negative regulators, GADD34. This is probably important for maintaining translation of interferon and interferon stimulated genes (ISGs), keeping ISA
-
In accordance with its original discovery EBI
2021-06-21
In accordance with its original discovery, EBI2 may play its major role in response to viral infections or in a pathological context such as in autoimmunity. Although we found a significant delay of onset in the Th17 transfer EAE model, active EAE was unchanged in absence of EBI2. At the moment, we
-
br Introduction Type Diabetes mellitus T DM
2021-06-21
Introduction Type 2 Diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a metabolic disorder that raises blood glucose level for a prolonged time. T2DM is associated with acute complications like ketoacidosis, hyposmolar coma, chronic complications include heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, foot ulcers and damage to
-
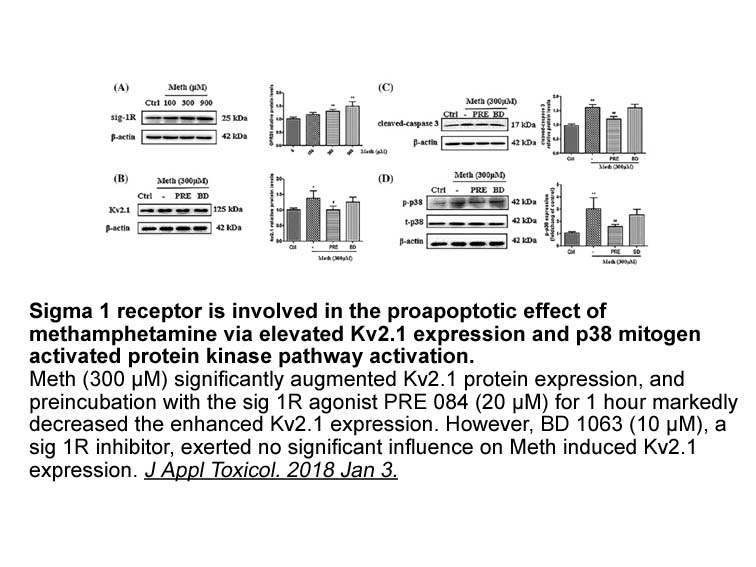
AMPHs facilitate dopamine release which further triggers
2021-06-21
AMPHs facilitate dopamine release, which further triggers dopamine depletion [72]. Indeed, we observed that repeated treatment of MPA significantly inhibited TH-, DAT-, and VMAT-2 levels. Since DAT and VMAT-2 are important for dopaminergic terminal markers [10], their decreases suggest that MPA-indu
-
br Development of the double strand
2021-06-21
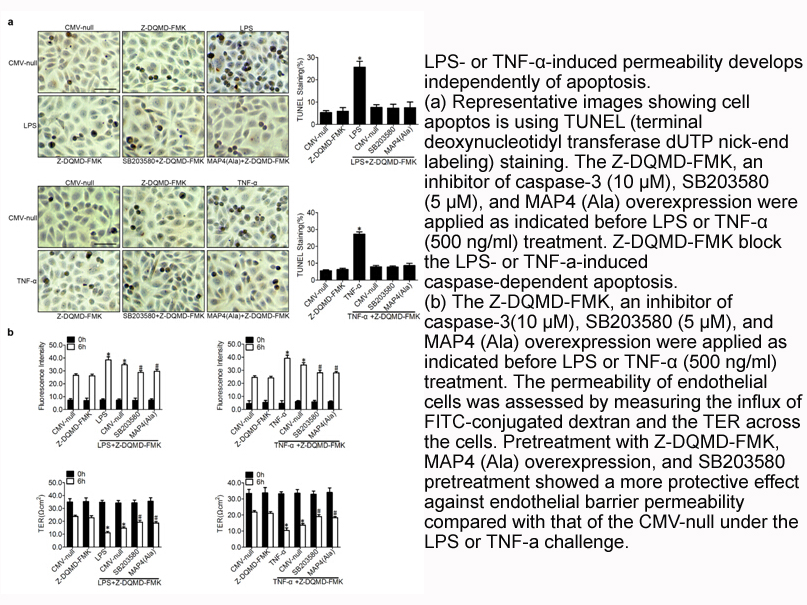
Development of the double strand break repair model for meiotic recombination Meiotic recombination was first described by Frans Alfons Janssens using prostaglandin receptor in the salamander Batracoseps attenuatus in 1909 [21] and then further elaborated at the genetic level in Drosophila by Th
-
In this study EDC NHS crosslinked collagen
2021-06-21
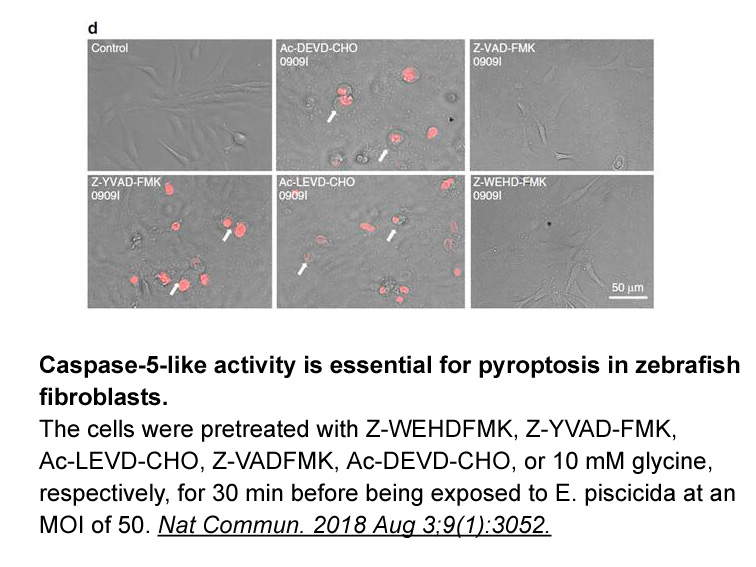
In this study, EDC/NHS crosslinked collagen films were derivatised with VWFIIINle-containing THPs and the effect on VWF and DDR2 activity was examined. First, we investigated restoration of the binding of DDR2 and VWF A3. Cell behavior beyond simple binding was also investigated through DDR2 RF 9 re
-
The IV chains of mature GBM are built
2021-06-21
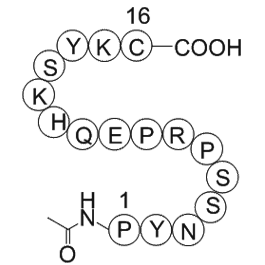
The α3/α4/α5(IV)-chains of mature GBM are built exclusively by podocytes (not by endothelial cells) (Abrahamson et al., 2009), placing the podocytes into the focus of GBM-diseases such as Alport syndrome. Alport syndrome (AS) is caused by mutations in the COL4A3, 4 or 5 genes coding for the α3/α4/α5
-
In order to assess quantitatively the
2021-06-21
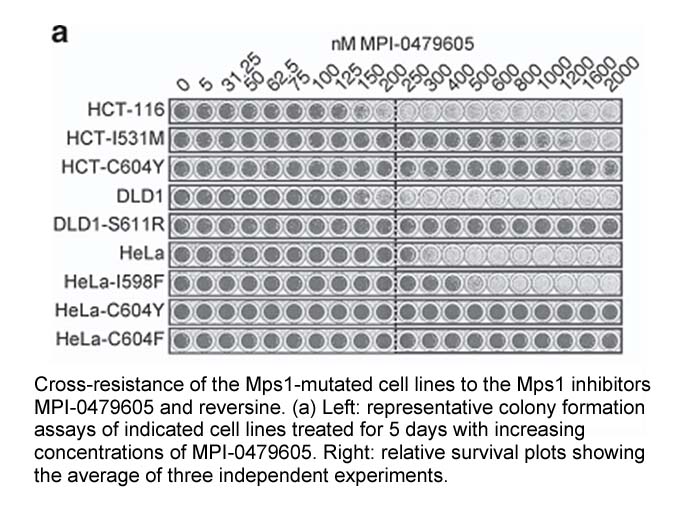
In order to assess quantitatively the contribution of the ung, dug and dut Aloperine to uracil-DNA accumulation in E. coli, we have developed a novel method for measuring uracil residues in DNA that is based on the approach of Kow and co-workers [33] for measuring AP-sites in DNA. The method, which
-
br NF B and STAT as Regulators of the
2021-06-21

NF-κB and STAT as Regulators of the CDK System While current data support the concept that CDKs augment the proinflammatory activity of NF-κB, our understanding of the function of this transcription factor system in CDK regulation remains patchy. Seminal studies showed the contribution of NF-κB t
-
As the principal receptors for regulating the inflammatory p
2021-06-21
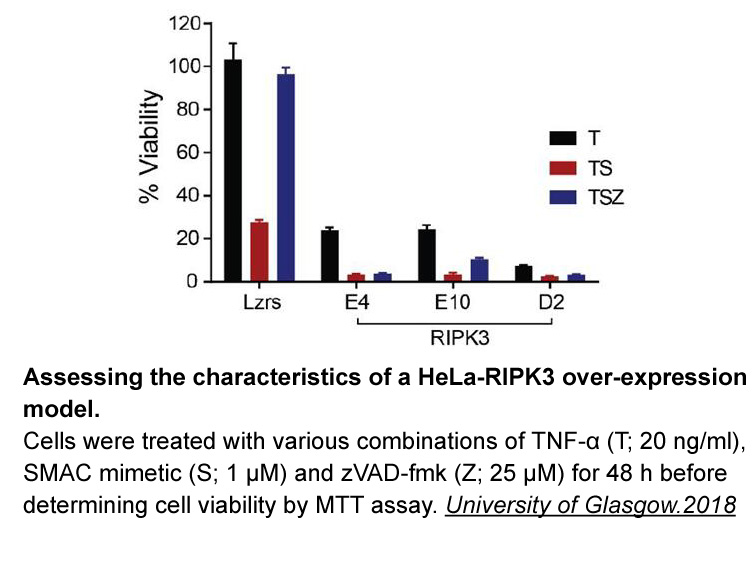
As the principal receptors for regulating the inflammatory process in mammals, CXCR1 and CXCR2 have an important role in regulating the trafficking of phagocytes such as neutrophils, monocytes and macrophages (Viola and Luster, 2008). The evidence gathered to date from fish studies are in agreement
-
The molecular mechanism by which CRM regulates IEC
2021-06-21
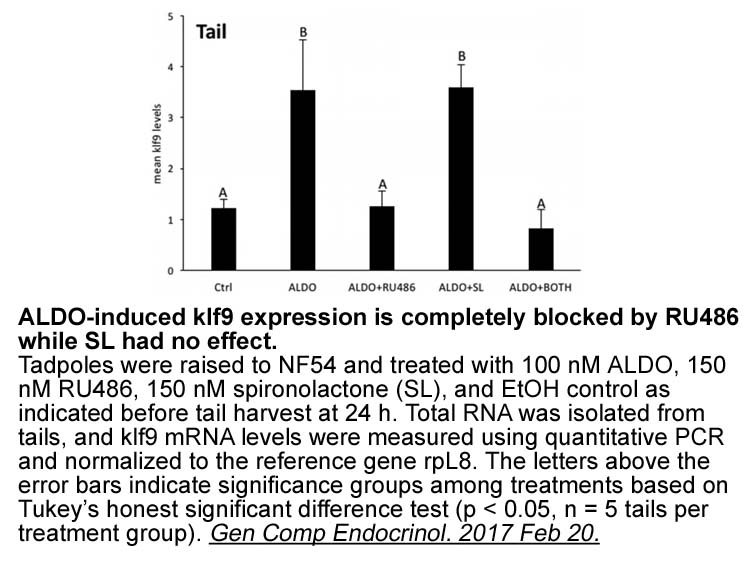
The molecular mechanism by which CRM1 regulates IEC apoptosis in CD remains to be explored. As an inhibitor of cyclin E-Cdk2, p27kip1 plays a pivotal role in controlling cell proliferation, S phase entry, and G1 phase exit during development and tumorigenesis [38]. As previously reported, p27kip1 is
14793 records 620/987 page Previous Next First page 上5页 616617618619620 下5页 Last page